Progress of Health and Population Sector 2021/22 (2078/79 BS) [National Joint Annual Review Report]
Overview
This report highlights the major progress of the health and population sector against its outcomes particularly over the last NHSS implementation year (Fiscal Year [FY] 2021/22), summarises lessons learned, and sets out the way forward for the next implementation period. Nepal has seen steady progress in health outcomes, particularly in life expectancy, child survival and maternal health during the NHSS implementation period. During FY 2021/22 priority was given to establishing new health facilities, strengthening existing facilities, enhancing quality related interventions such as minimum service standards (MSS) and roll out of standard treatment protocol for basic health services, and equitable distribution of health services.
Progress in major health indicators
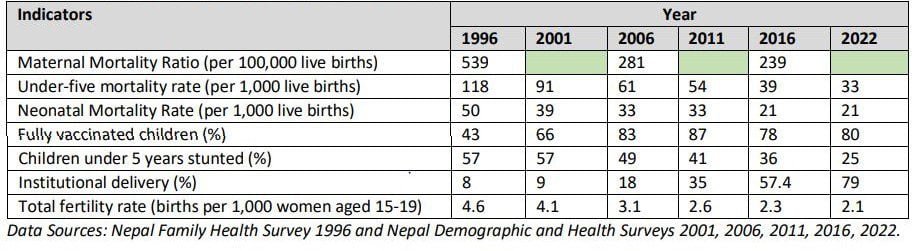
Major achievements
The major achievements of the health and population sector in the FY 2021/22 were:
Strategies
- Finalisation of the “Nepal Health Sector-Strategic Plan (NHS-SP) 2022-2030” which has been proceeded for the endorsement. This sets the priorities and implementation framework for the sector as an operational plan of the National Health Policy, 2019 and an instrument of the SWAp in alignment with the sustainable development goals (SDGs)
- Final draft of National Health Financing Strategy was developed in November 2021 through a participatory approach adopting rapid results initiatives and was proceeded for the endorsement.
- National Strategy on Human Resources for Health 2020/21- 2029/30 was endorsed by the FMoHP in 2021. This new strategy assesses the situation of the HRH in Nepal and sets roadmap for the management of the human resources for future.
Information Management and surveys
- The Integrated Health Information Management System (IHMIS) roadmap (2022-2030) has been endorsed in 2021. The roadmap aims to initiate coordinated mechanism for health information management for various health information systems and increase the use of information and digital technology management.
- As envisioned in the IHMIS Roadmap, all HMIS tools have been revised after 9 years to align with ongoing health sector programmes and services, and their implementation have also been initiated from current FY.
- The FMoHP continued to expand the electronic reporting of service data from HFs. In FY 2021/22, altogether 2,970 public health facilities submitted HMIS monthly reports electronically.
- The final report of the Nepal Health Facility Survey (NHFS) 2021 has been published. The NHFS 2021 collected information from all different types of public, private and non governmental facilities covering all 77 districts of the country.
- The Nepal Demographic and Health Survey (NDHS) 2022 has been completed, and its major findings has been disseminated in November 2022.
- MoHP has been conducting a maternal mortality study basing on the Nepal Population and Housing Census (NPHC). While the data collection was accomplished following the population census, data analysis is being done. This study is expected to provide the robust estimates of the maternal mortality in Nepal and can be supportive to design necessary interventions to reduce such mortalities.
Epidemic response (COVID-19 and Dengue)
- The daily monitoring, reporting and dissemination of COVID-19 (and Dengue for the latest months) status is being continued by the national Health Emergency Operations Centres (HEOCs) in coordination with concerned entities. Provincial HEOCs are functional in each of seven provinces.
- The number of reported cases of COVID-19 has reduced. Progress has been made in vaccine coverage after the vaccination campaign officially started on 27 January 2021. The booster dose of COVID-19 was initiated in January 2022. The guideline for vaccination against COVID-19 among the group 5 to 11 years was developed, and the vaccination was initiated to that age group.
- As of September 2022, 99.5% of the target population above 12 years (23,208,483) have received the first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine, and 95.7% (22,324,933) have received the full dose.
Procurement and supply chain management
- The Public Procurement Strategic Framework (PPSF) for Management of Medicines and Medical Goods (2022/23-2026/27) has been endorsed to address the challenges related to procurement and supply chain management.
- The process of developing Consolidated Annual Procurement Plan (CAPP) has been institutionalised at the Department of Health Services (DoHS). The electronic CAPP for the FY 2021/22 was prepared on time.
- After the transformation of the federal procurement implementation plan (PIP) into the PPSF, the three provinces (Madhesh, Lumbini and Sudurpaschim) prepared their respective PIPs coherent with the federal PPSF.
- The capacity development of the officials working on procurement and supply chain management through facilitation, procurement clinics, on-site coaching, and distance support were continued throughout the year. The orientation sessions were organised on costestimate, specification preparation, and bid evaluation in health sector procurement to the officials of Departments, Centres and Hospitals.
Infrastructure, assets management and service standards
- A total of 467 designs were received for the establishment of Basic hospitals (primary level) by the end of October 2022, of which 178 have been approved; the rest are being updated for resubmission of revised drawings.
- The inventory audit of 54 hospitals was conducted using Planning and Management of Assets in Health Services (PLAMAHS) in the FY 2021/22 and audit of additional 80 hospitals has been planned for the FY 2022/23.
- Over the period from July 2021 to April 2022, FMoHP conducted various capacity enhancement events on health infrastructure, involving a total of 146 participants despite the restrictions created by the COVID-19 pandemic
- Public hospitals and health facilities were assessed using MSS to improve the quality of health services. A digital data system was established to monitor the MSS score in FY 2021/22. The MSS score of a total of 118 hospitals comprising of federal, provincial and local level hospitals has been systematically monitored.
- The Department of Ayurveda and Alternative Medicine (DoAA) developed the MSS for different levels of Ayurveda institutions (Federal, Provincial, District and Aaushadhalaya) and their implementation has been initiated Standard treatment protocols (STP) for basic health services and emergency health services were finalised was endorsed in 2021 and orientation was conducted for their implementation
- A guideline for the disposal of medicine and medicinal waste has been developed to address the emerging issue of environmental and health hazards, and has been endorsed and distributed to all health institutions, provincial and local governments.
One-stop Crisis Management Centres (OCMCs), Social Service Units (SSUs) and Geriatric Health
- Eight additional One-stop Crisis Management Centres (OCMCs) were established in 2021/22 which makes a total of 88 OCMC sites in 77 districts. In FY 2020/21, 11,400 survivors received services from the OCMCs. Six more OCMCs are planned for 2022/23. SSUs are operationalised in 58 hospitals and FMoHP has planned for an additional 29 SSUs in FY 2022/23.
- The OCMCs provide free hospital-based health services including identification of survivors, treatment, psychosocial counselling, and medico-legal services, and coordinate with multisectoral agencies that provide survivors access to safe homes, legal protection, personal security and rehabilitation. They also refer clients for specialist health services as required.
- Fifty OCMC staff nurses have been certified as psychosocial counsellors after successful completion of six-month long psychosocial counselling training from the National Health Training Centre (NHTC) and 40 OCMC focal persons are in-process to complete the counselling course to become certified counsellors.
- Fifteen new Social Service Units (SSUs) were established in referral and district-level hospitals; the total number of SSUs has gone up to 58. More than 200,000 beneficiaries (Female 50%; Poor 47%, Senior Citizens 39%, People with disabilities 4%, Destitute 3.8%; GBV survivors 0.6% and others) received free or partially free service in 2021/22 from 58 SSUs. The FMoHP plans to establish new SSUs in 29 hospitals in FY 2022/23.
- An additional twenty-five geriatric wards were established in different-level hospitals in 2021/22 making a total of 49 hospitals with geriatric wards. The FMoHP has the plan to establish new geriatric health services in 12 hospitals in FY 2022/23.
- Geriatric Health Service Strategy (2078), Leave No One Behind (LNOB) Budget Marker Guideline for the health sector (2078), SSU Operational Guideline (2078), Geriatric Health Service Operational Guideline (2077), Geriatric Health Service Protocol (2079) have been developed/revised and endorsed.
Training and mentoring
- The National Nursing and Midwifery Strategic Action Plan 2020-2030 has been developed with a projection of the nursing and midwifery workforce required to provide quality services
- The NHTC developed training materials for 13 different areas; essential critical care, paediatric essential critical care, integrated training for vector-borne diseases, screening for infertility, ambulance driver, basic emergency medical technician training, social accountability, disability-related training for medical officers, management training for health section chiefs at the local level, orientation for elected bodies at the local level, acute respiratory distress syndrome management, public health leadership.
- The NHTC has revised five existing training materials: Rural obstetric ultrasound training, infection prevention (IP) training, Voluntary Surgical Contraception (VSC)/minilap training for MDGP/OBGYN/Surgeons, basic Intensive Care Unit (ICU) training for nurses, first-trimester safe abortion training for MDGP/OBGYN.
- NHTC conducted 29 different types of training of trainers and basic training through which 10,882 human resources were trained.
- The Family Welfare Division (FWD) and NHTC/ Provincial Health Training Centre (PHTC) trained 61 MNH clinical mentors from province one, Gandaki, Karnali, Madhesh, Sudurpashchim and Lumbini province, and established clinical mentors training sites at Surkhet provincial hospital Karnali province, Pokhara academy of Health Science, Gandaki Province and Janakpur Provincial hospital.
- The Nursing and Social Security Division (NSSD) started clinical mentoring of nursing staff on routine nursing care at six federal hospitals. A learning resource package for nursing mentoring covering nine areas was developed, thirteen mentors were developed, and 165 nursing staff received in-house mentoring.
- The training package on Gender Responsive Budgeting (GRB) and LNOB Budget Marker was finalised and approved by FMoHP. Based on this training package, training was provided to health staff from 5 provincial health ministries at NHTC.
Service expansion
- The health insurance scheme is being implemented in all 77 districts with exception of some local levels in Kathmandu. Approximately 20.4% of the population have enrolled in the scheme by the end of 2021/22 while there was 28.9% drop out. Health Insurance Board (HIB) has initiated online systems for the renewal and has planned to initiate online enrolment.
- The National Ambulance Guideline 2021 has been developed and endorsed to facilitate effective and timely referral of complicated cases. The guideline aims to strengthen prehospital care services and defines different categories of ambulance services.
- The Department of Ayurveda and Alternative Medicine (DoAA) published the implementation plan and handbook for the effective implementation of Citizen Wellbeing Programme (Nagarik Aarogya Karyakram). Healthy lifestyle management programme under Nagarik Aarogya Karyakram (Citizen Wellbeing Programme) was conducted from 380 Ayurveda health institutions and 298 citizen wellbeing centres.
- Around 7,700,000 children received vaccination against Typhoid through Typhoid vaccination campaign, and Typhoid vaccination has been integrated to routine immunisation programme
- The TB Free Nepal Declaration Initiative was initiated in 25 local governments based on the TB Free Nepal Declaration Guideline 2020/21.
- A non-Communicable Diseases (NCD) multisector action plan has been endorsed and a guideline has been prepared to facilitate the NCD screening.
- The National Health Education, Information and Communication Centre (NHEICC) launched the SAFER initiative that include: Strengthening restrictions on alcohol availability; Advancing and enforcing drink driving counter measures; Facilitating access to screening, brief interventions and treatment; Enforcing bans or comprehensive restrictions on alcohol advertising, sponsorship, and promotion; and Raising prices on alcohol through excise taxes and pricing policies;
- The Gender Equality and Social Inclusion (GESI) strategy of Madhesh province was developed and approved by the provincial government. A number of activities in the strategy were included in the Annual Workplan and Budget (AWPB) for implementation.
- Lumbini province conducted an assessment on disability-inclusive health services at hospitals and health centres. The findings of the assessment were included in the current AWPB on a priority basis.
Recommended readings
- Progress of the Health and Population Sector, 2019/20
- Progress of the Health and Population Sector, 2020/21 (NJAR Report)
- Annual Report of the Department of Health Services (DoHS) 2077/78 (2020/2021)
- Nepal Health Sector Strategy (NHSS) Mid Term Review Report
- Preliminary Findings: Nepal Health Facility Survey 2021


