National Joint Annual Review Report – 2020 (2077 BS) #NJAR2020
Major Achievements
The major achievements of progress in FY 2019/20 are summarised below:
- The National Health Policy, 2076 (2019) has been endorsed by the Cabinet of Ministers. The policy includes 25 policy statements, each with multiple strategies.
- The Cabinet of Ministers has endorsed the Public Health Service Regulations 2020, the Safe Motherhood and Reproductive Health Rights Regulations 2020 and the Health Insurance Regulation 2019.
- Health human resources have been deputed as per the federal structure of governance. An adequate response to the COVID-19 pandemic has been provided.
- Health services are offered from health facilities despite the challenges posed by COVID-19 Pandemic.
- Gender-responsive Budget Guidelines for the health sector was developed and approved. Prepared the final draft of National Strategic Plan for 2021–2026 (National Tuberculosis Programme) has been prepared.
- Pre-bid and post-bid information systems, including Market Analysis (MA), electronic Technical Specification Bank (e-TSB) strengthening, electronic Logistics Management Information System (e-LMIS) reforms, Grievance-handling and Redressal Mechanism (GHRM) installation and online electronic Consolidated Annual Procurement Plan (e-CAPP) modules in the Transaction Accounting and Budget Control System (TABUCS) have been endorsed and implemented.
- As agreed in the NJAR 2019, the concept of transforming the Procurement Improvement Plan (PIP) into an umbrella strategic document on procurement and Supply Chain Management (SCM) is being progressed by drafting the Nepal Health Sector Public Procurement Strategic Framework (NHSPPSF).
- Updating of the Financial Management Improvement Plan FMIP into the Public Financial Management Strategic Framework (PFMSF) has been completed and the PFMSF is in the process of being endorsed.
- Two sets of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for procurement and electronic Government Procurement (e-GP) have been endorsed in FY 2018/19 and their implementation continues across the three levels of government.
- Emergency Procurement Guidelines have been drafted and are now in the course of endorsement by MoHP.
- Standardisation of the procurement process through new Standard Bid Documents (SBDs) and e-GP-II implementation in the bidding process has been improved and put into practice. This electronic bidding system, executed as e-GP in FY 2019/20, has increased the proportion of procurement carried out electronically to the highest recorded level: 98 per cent of CAPP value, compared to 83 per cent in e-GP for FY 2017/18.
- Audit queries against total audit amount have been reduced from 7.01 per cent (in FY 2016/17) to 4.77 per cent (in FY 2017/18). However, this figure increased to 6.73 per cent (in FY 2018/19).
- Charts of activities have been prepared and are ready to be used in TABUCS.
- Five district hospitals have been upgraded to 25-bed hospitals, while all remaining district hospitals have been upgraded to 50-bed hospitals. Provincial hospitals are being upgraded to have 200 beds and hospitals under the federal government are being upgraded to have 500 beds.
- As per the Government of Nepal’s (GoN’s) policy of ‘one municipality-one hospital’, budget has been sent to 396 local levels to establish 5-, 10- and 15-bed basic health care hospitals. Foundation stones for more than 300 hospitals were laid down on a single day (November 30, 2020).
- Establishment of a 300-bed communicable diseases control hospital at federal level, and similar 50-bed hospitals in each province, has been initiated.
- The work for establishing 10 trauma centres is ongoing (5 million Nepalese Rupees (NPR) has been allocated to each hospital), and free emergency services are being provided from 14 public sector hospitals.
- Extensive and unprecedented response actions are being undertaken to mitigate the effects of COVID-19.
- The Programme Implementation Guideline for FY 2020/21 (for the programme of provincial- and local-level activities) was prepared and made public through the MoHP website.
- About 3.3 million people in total have enrolled in the health insurance scheme, which is being implemented in 60 districts and 471 local levels.
- The MA of Pharmaceutical Products in Nepal was designed, and accompanying survey completed, by October 2019. The final report was distributed in FY 2019/20 to all stakeholders.
- In response to COVID-19, technical specifications of equipment to be installed in the e-TSB have been prepared.
- The Federal CAPP (FCAPP) was prepared and endorsed in FY 2018/19 and implementation progress is being monitored by the Public Financial Management (PFM) Committee of MoHP and CAPP Monitoring Committee of DoHS. Online preparation of the federal e-CAPP was initiated in FY 2018/19 and the executed e-CAPP for FY 2019/20 captures 97 per cent of the total procurement budget of the MoHP.
- The Internal Control Guidelines have been drafted as the New Financial Procedures and Fiscal Accountability Act, 2076 (2019) and Financial Comptroller General Office (FCGO) directives.
- The FMIP has been updated as the Nepal Health Sector Financial Management Strategic Framework, to guide financial management procedures. The framework was endorsed by the Minister of MoHP (on 2077.04.04/19 July 2020) and has been printed and disseminated; its implementation continues across federal-level entities.
- The Financial Management Reports (FMRs) for each trimester of FY 2019/20 were submitted on time. Improved internal control through internal and final audit clearance was evidenced in the Audit Status Report prepared in August 2020, which was disseminated to External Development Partners (EDPs).
- Provincial reviews of the health sector in all seven provinces have been completed.
- MoHP secured funding from the Global Environment Facility to implement the project entitled Building Resilience of Health Systems in Asian Least Developed Countries to Climate Change.
- Seven additional One-stop Crisis Management Centres (OCMCs) have been established in the first quarter of 2077/78 (2020/21), which makes a total of 77 OCMC sites in 74 districts. Similarly, six Social Service Units (SSUs) were established in the first quarter of 2077/78 in referral and district-level hospitals; the total number of SSUs has gone up to 44.
- Geriatric health services are available in 24 hospitals as of the first quarter of 2077/78.
- Health Emergency Operations Centres (HEOCs) are functional in each of the seven provinces, cluster coordination mechanisms activated, and different guidelines/SOPs developed which, played a crucial role in the management of the COVID-19 response.
- Reconstruction of the structures of 15 Health Posts (HPs) damaged by the earthquake has been completed by National Reconstruction Authority (NRA).
- An Annual Report on Population for FY 2018/19 has been produced, highlighting major progress in this sub-sector.
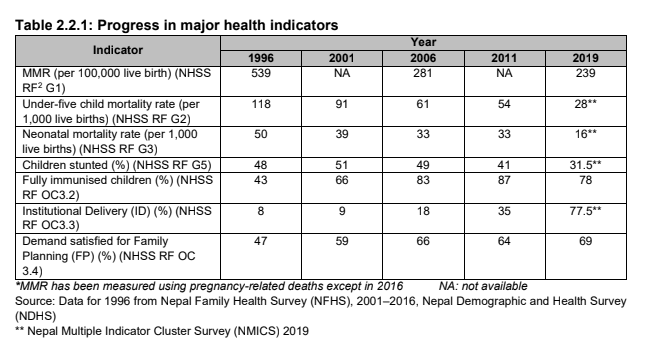
Progress in major health indicators



1 comment
Good info and straight to the point. I am not sure if this is in fact the best place to ask but do you folks have any ideea where to get some professional writers? Thanks 🙂
Comments are closed.