The Department Health Services (DoHS) Annual Report 2078/79 has released it’s annual report for the fiscal year 2078/79 (2021/22. The annual report of the Department of Health Services (DoHS) for fiscal year 2078/79 (2021/2022) is the twenty-eight consecutive report of its kind. This report focuses on the objectives, targets and strategies adopted by Nepal’s health programs and analyses their major achievements and highlights trends in service coverage over three fiscal years. This report also identifies issues, problems and constraints and suggests actions to be taken by health institutions for further improvements.
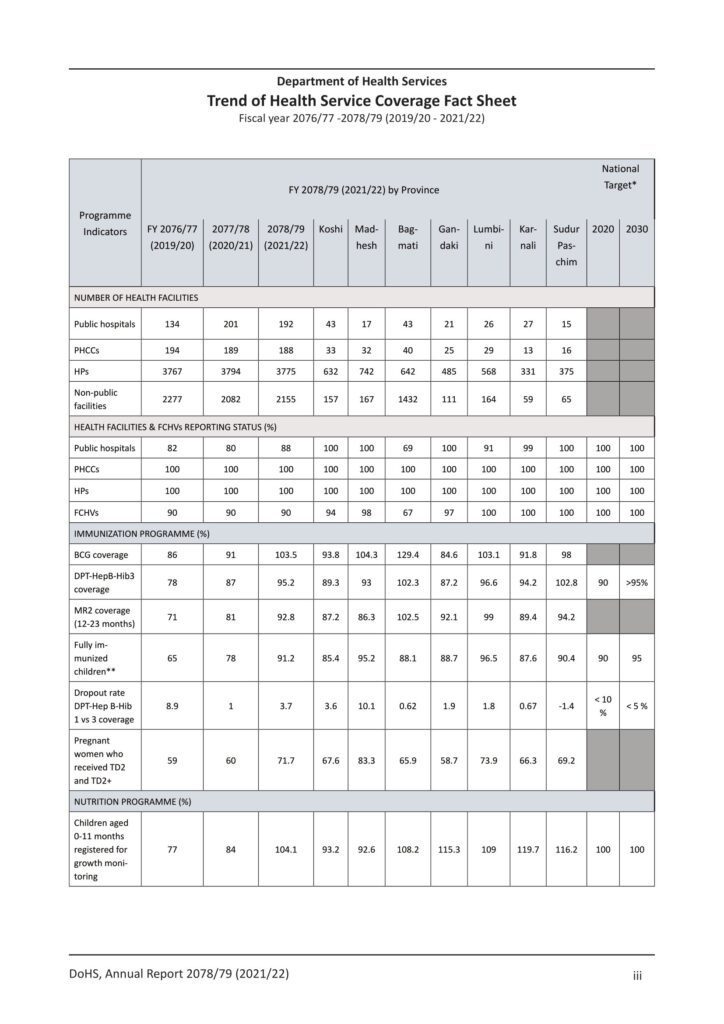
The main institutions that delivered basic health services in 2078/79 were the 192 public hospitals including other ministries, the 2,155 non-public health facilities, the 188 Primary Health Care Centers (PHCCs) and the 3,775 Health Posts (HPs) primary health care services were also provided by Primary Health Care Outreach Clinic (PHC-ORC) sites. A total of 16,950 Expanded Program of Immunization (EPI) clinics provided immunization services. These services were supported by 50,229 Female Community Health Volunteers (FCHV). The information on the achievements of the public health system, NGOs, INGOs and private health facilities were collected by DoHS’s Health Management Information System (HMIS).
Executive summary
National Immunization Program (NIP)
- In FY 2078/79 compared to FY 2077/78, BCG coverage improved by 13%, whereas DTP-HepB-Hib3 and OPV3 coverage increased by 10% and 13% respectively. The fIPV2 coverage rate has increased to 93% for FY 2078/79. PCV3 coverage has increased to 94%, and PCV1 coverage has reached 98%. Coverage for MR1 and MR2 is now 95% and 93%, respectively.
- High coverages of both MR1 and MR2 are necessary (> 95%) at all levels to achieve measles eradication. As a result, MR1 and MR2 coverage still has to be increased. The JE vaccination coverage is 96% at national level.
Integrated Management of Neonatal and Childhood Illnesses
- Among all reported live births, chlorhexidine (CHX) was administered to 82.9% of newborns’ umbilical cord (HF+ FCHV).
- Use of CHX varied by province, with Sudurpaschim having the highest use (96.9%) and Bagmati Province having the lowest use (64.7%). At the national level, injectable Gentamycin was given to all PSBI cases involving infants under two months old in the fiscal year (FY 2078/79).
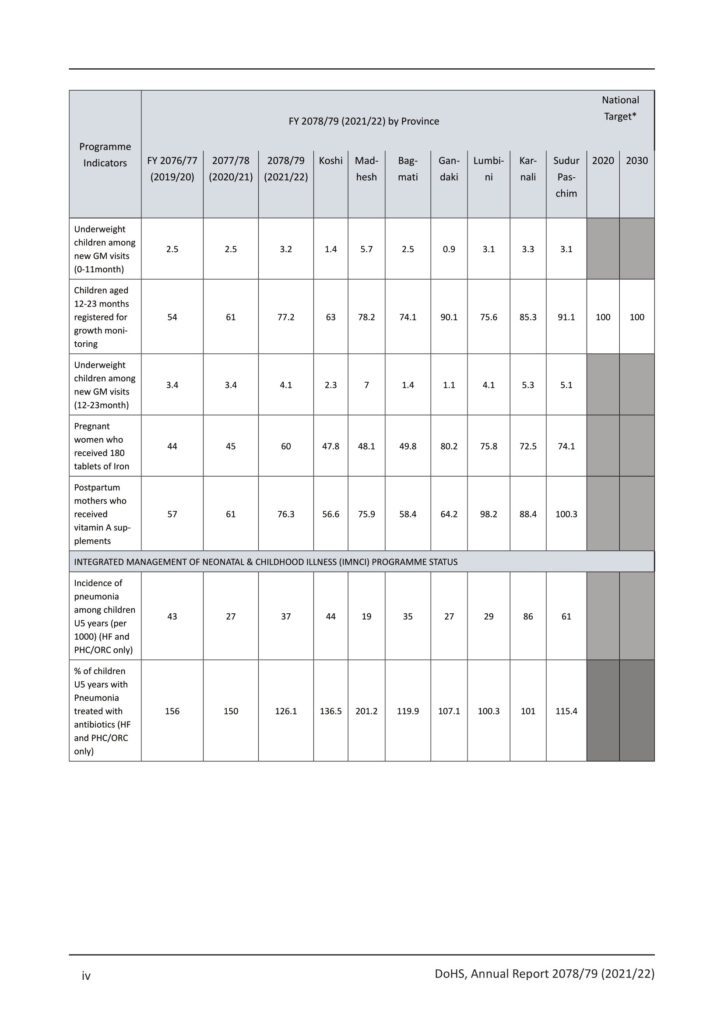
- A total of 702,504 ARI cases were reported at HF and PHC/ORC in FY 2078/79, of which 13.3% were classified as pneumonia and 0.18% as severe pneumonia. At the national level, there were 55.1 cases of pneumonia (both mild and severe) per 1000 children under the age of five.
Nutrition
- The growth monitoring visit has increased by 25.5 percentage points at the national level from FY 2076/77 (65.2%) to FY 2078/79 (90.7%). A significant reach of Growth Monitoring and Promotion (GMP) among the targeted age group is also demonstrated by the coverage of GMP registration across the seven (7) Provinces, with Provincial values ranging from a low of 78.1% in Province No. 1 to a high of 103.7% in Sudurpaschim Province. In FY 2078/79, the Mother Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative (MBFHI) program was assessed in 10 hospitals, and orientation was done in additional five hospitals.
- Until FY 2078/79, 15 MBFHI hospitals have been certified. By the end of FY 2078/79, the CNSI training package has been rolled out in 72 districts and five districts of Bagmati province are planned for FY 2079/80.
Safe Motherhood and Newborn Health
- Maternal and Newborn Health (MNH) is a high-priority program in Nepal. The National Safe Motherhood Programme implemented by Family Welfare Division (FWD) aims to reduce maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality, improve maternal and neonatal health through preventive and promotive activities, and address avoidable factors that cause death during pregnancy and childbirth and the postpartum period.
- In FY 2078/79, there was a significant increase in key Maternal and Newborn Health (MNH) indicators.
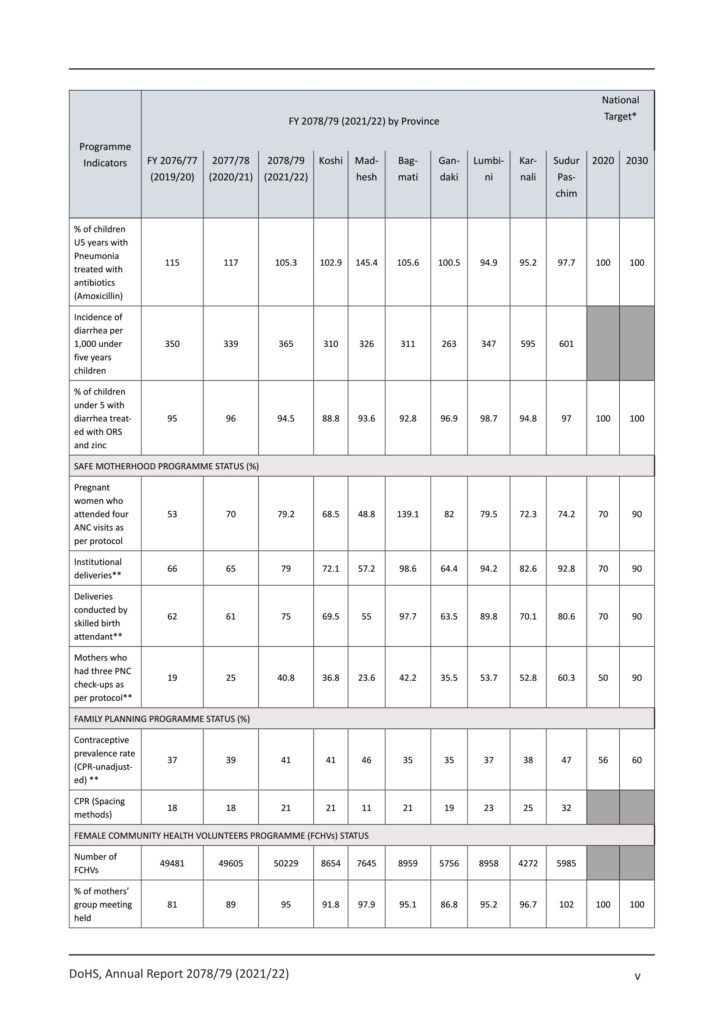
- The percentage of pregnant women attending 4 ANC visits as per the protocol increased to 79.4 in FY 2078/79 from 70 in 2077/78. Similarly, institutional deliveries as a percentage of expected live births increased by 14%.
- Furthermore, the delivery assisted by SBA increased to 75% in FY 2078/79 from 61% in FY 2077/78.
- The national average for Emergency Obstetric Care (EOC) met needs was 11% in this reporting period, improving from 8.2% in FY 2077/78. The proportion of mothers attending three PNC visits as per the protocol increased from 25% in FY 2077/78 to 40.8% in FY
- 2078/79.
- Although there is improvement in key MNH indicators, major gaps in quality of care exist along the continuum of care such as 4 ANC visits and 3 PNC as per the protocol. Similarly, considerable interprovincial gaps were noticed in the quality of care, with around 32% difference in the proportion of women receiving 180 days’
- supply of Iron Folic Acid (IFA) during pregnancy, with 80.2% of women receiving it in Gandaki Province while only 47.8%
- in Koshi Province in the year 2078/79.
- The number of safe abortion service users increased to 90,733 in FY 2078/79 from 79,952 in FY 2077/7 and 87,869 women in FY 2076/77.
- Among these, 69% were medical abortions, and 31% were surgical abortions in FY 2078/79. 14.2% of the total pregnancies were terminated by induced procedures at health facilities, and 4.4% were induced using the surgical method. Although the safe abortion service users increased in FY 2078/79, the post-abortion contraception has slightly decreased to 74.7% in FY 2078/79 from 76.7% in FY 2077/78.
- Among the safe abortion users, approx. 7% of the women were aged below 20 years.
- In FY 2078/79, FWD implemented the MPDSR program in 32 districts and 94 hospitals.
- In FY 2078/79, a high percentage of maternal deaths were reported in the antepartum period (34%) followed by the postpartum period after 48 hours of delivery (31%).
- FWD also implemented various activities in FY 2078/79 to improve maternal and child health, such as expansion and quality improvement of BEONC and CEONC sites, onsite clinical coaching and mentoring, MNH readiness assessment and emergency referral funds. In this reporting period, 753 municipalities of 77 districts implemented onsite clinical coaching and mentoring programs, and a quality improvement process programme expanded in 65 hospitals.
Family Planning and Reproductive Health
- National family planning programme (FP) in 2078/79 has been successful to improve the service access and utilization.
- The modern contraceptive prevalence rate (unadjusted mCPR) for modern FP at national level is 41% compared to 39% in FY 2077/78.
- Sudurpaschim Province has the highest mCPR of 48% while Bagmati Province has the lowest (35%). The number of districts with mCPR below 30% is in a decreasing trend.
- In FY 2078/79, there are 5 districts with CPR less than 30 compared to 9 in FY 2077/78.
- This indicates performance improvement among the low mCPR districts. Depo (38%) occupies the greatest part of the contraceptive method mix for all method new acceptors, followed by condom (23%), pills (19%), implant (14%), IUCD (2%), female sterilization (FS- 3 %) and lastly male sterilization (MS-1%) in FY 2078/79.
- Immediate postpartum family planning uptake as proportion of total facility delivery is in increasing trend.
- Postpartum IUCD uptake as proportion of total facility delivery is also in decreasing trend, while that of contraceptive
- uptake among total reported abortion services is 71%, but only 15% have used LARCs indicating women after abortion are relying on less effective methods.
Adolescent sexual and reproductive health
- Adolescent Sexual and Reproductive Health (ASRH) is one of the priority programs of FWD guided by The National Adolescent Health and Development Strategy, 2018. The National ASRH program has been scaled up to all 77 districts by Fiscal Year 2078/79. So far, about 1,355 health facilities have been listed and 116 health facilities have been certified as adolescent friendly service sites.
- The number of adolescents receiving temporary contraceptive methods (excluding condom) is in decreasing trend.
- Among four temporary contraceptive methods, Depo is the most preferred contraceptive method accounting for 58% of the contraceptive method mix. Compared to FY 2077/78, the share of implants in method mix has decreased.
- Similarly, utilization of abortion services is also in decreasing trend. This data needs to be cautiously interpreted as adolescents prefer to utilize the sexual and reproductive health (SRH) services from the private sector due to several reasons. It is interesting to note that the share of medical abortion services is decreasing. Almost two-thirds of adolescents (61%) who terminated the pregnancy opted for medical abortion.
- In FY 2078/79, Madhesh Province had the highest number of adolescents who received first ANC services and first ANC visit as per protocol. Whereas Gandaki Province has the lowest number of adolescents receiving ANC services.
- At the national level, the dropout rate between ANC 1st and ANC 4th visits is around 33% in FY 2078/79 which is lower than the previous year.
- Primary Health Care Outreach Clinics
- Primary health care outreach clinics (PHC/ORC) extend basic health care services to the community level. In FY 2078/79, 2,289,178 people were served from outreach clinics. Out of planned clinics, 86% were conducted.
- There has been a slight increase in the conduction of PHC-ORC Clinics and clients served compared to previous year.
- Malaria
- Nepal has surpassed the Millennium Development Goal 6 by reducing malaria morbidity and mortality rates by more than 50% in 2010 as compared to 2000. Therefore, the Government of Nepal has set a vision of Malaria free Nepal by Current National Malaria Strategic Plan (NMSP) 2014-2025 was developed based on the epidemiology of malaria derived from 2012 micro-stratification. The aim of NMSP is to attain “Malaria Free Nepal by 2025”.
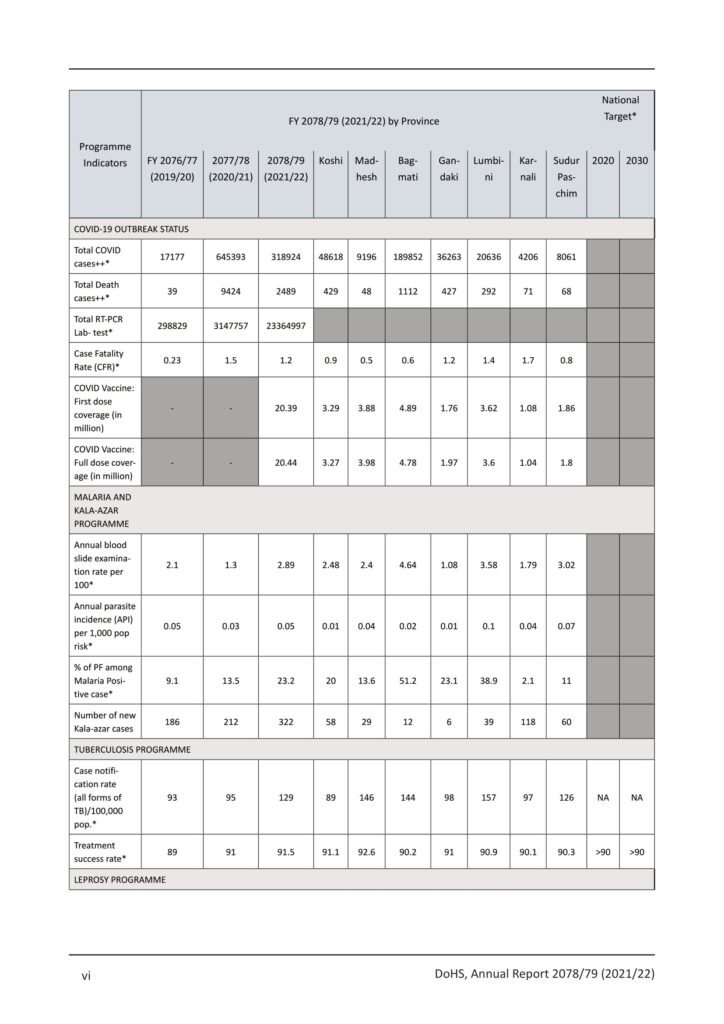
- For assessing the risk areas, the program has been conducting micro-stratification on an annual basis. Total positive cases of malaria increased from 377 in FY 2077/78 to 491 in FY 2078/79 to, where 38 cases are indigenous cases and 453 are imported.
- The trend of indigenous is decreasing, however, the number of imported cases is increasing.
- As compared to the previous year, the proportion of P. falciparum infections has increased from 13.53% in FY 2077/78 to 23.2% in 2078/79. This proportion is high which is due to the high number of imported P. falciparum cases mostly from India and the Central Africa Region (CAR).
- The trend of indigenous Pf malaria cases is decreasing. In FY 2078/79, all PF cases were imported. The trend of clinically malaria cases is slightly increasing and major indicators for malaria program; Test positivity rate (TPR), and Annual Blood Examination Rate (ABER) are in positive trend, however, Annual Parasite Incidence Rate (API) has slightly increased.
Kala-azar
- Kala-azar is one of the high priority public health problems of Nepal. Most of the districts have been continuously reported new cases of Kala-azar in recent years. Therefore, to eliminate Kala-azar from Nepal, strategies to improve health status of vulnerable and at-risk populations have been made focusing on endemic areas of Nepal, which leads to elimination of Kala-azar, and it no longer becomes a public health problem. The incidence of kala-azar at national level has
- been less than 1/10,000 population since FY 2073/74. However, the trend of Kala-azar cases has been increasing in a few
- years. In FY 2078/79, two districts, Okhaldhunga and Kalikot, crossed the elimination threshold with 1.62 per 10,000 in Okhaldhunga and 4.14 per 10,000 in Kalikot.
Lymphatic filariasis (LF)
- Lymphatic Filariasis (LF) is one of the mosquitoes borne parasitic diseases with a public health problem in Nepal.
- Nepal is among the countries who have started LF MDA in all endemic districts and is on track to achieve elimination status by The goal of the Lymphatic Filariasis Elimination Program is to eliminate LF as a public health problem by reducing the level of the disease in the population to a point where transmission no longer occurs.
- As of Poush 2079, MDA has been stopped and post MDA surveillance is ongoing in 48 of 64 endemic districts.
- All endemic districts completed 6 rounds of MDA in 2075 other than Rasuwa which has recently been considered endemic from a confirmatory mapping survey.
- Triple Drug Regimen (IDA: Ivermectin, Diethylcarbamazine and Albendazole) has been introduced in 5 districts from 2078 and EDCD has planned to expand it in all 15 districts that will implement MDA in 2079.
- Since 2060 more than 115 million doses of lymphatic filariasis drugs have been administered to at-risk populations.
- A total number of 10,477 hydrocele surgeries have been performed since FY 2073/74 to FY 2078/79.
- The morbidity results by community mapping from 44 districts revealed that 30,925 cases of LF have been confirmed of which 21,105 cases of hydrocele, 9,574 cases of lymphoedema and 246 cases of both conditions.
Dengue
- Dengue, a mosquito-borne disease, emerged in Nepal in 2062. The goal of the national Dengue control program is to DoHS, Annual Report 2078/79 (2021/22) reduce the morbidity and mortality due to dengue fever, dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) and dengue shock syndrome (DSS).
- The number of reported dengue cases has decreased significantly since 2066 but cases of dengue have increased in recent years. During FY 2078/79, a total of 733 dengue cases were reported from 62 districts.
- The majority of cases have been reported from Sankhuwasabha (79), Kathmandu (65), Dhading (55), and Rupandehi (44).
Scrub Typhus
- After the devastating earthquake in 2072, outbreak of scrub typhus has been reported from across the country causing several morbidities and mortalities. Although the surveillance system for scrub typhus is not very well established, the scrub typhus cases were reported through the early warning and reporting system (EWARS) from 2073.
- During FY 2078/79, a total of 2,474 dengue cases were reported from 71 districts. The majority of the cases have been reported from Doti (288), Darchula (222), Palpa (205), Kailali (160), Gulmi (133), Baitadi (124) and Sankhuwasabha (101).
Leprosy
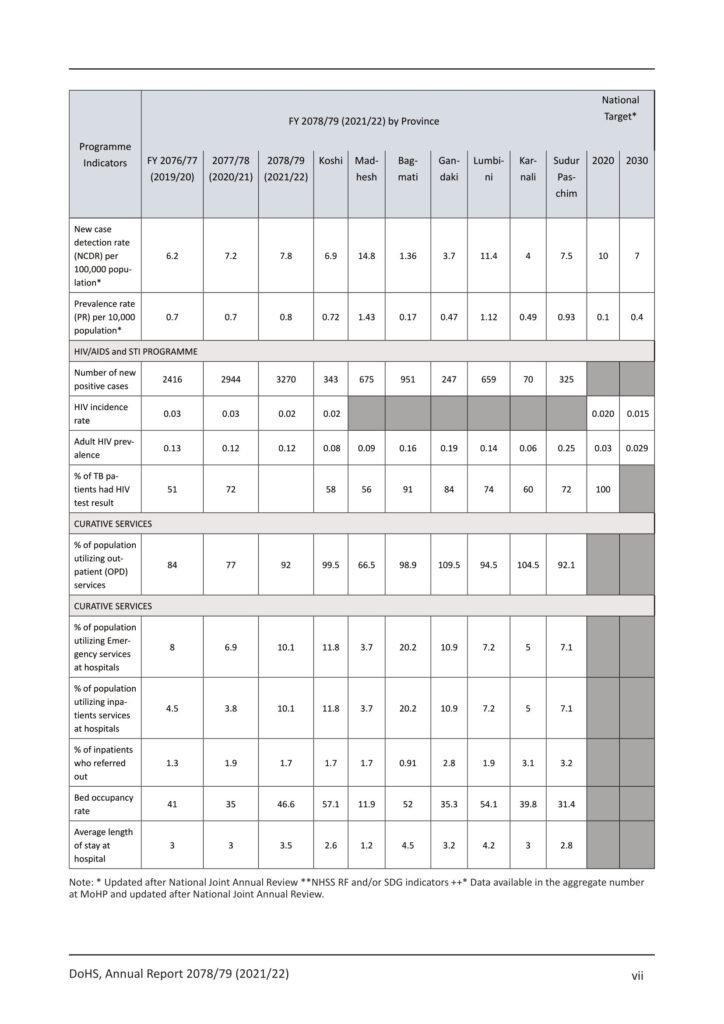
- During FY 2078/79 (2021/22), 2285 new leprosy cases were detected and put under Multi Drug Therapy (MDT) from 64 districts. Among total new cases, 3.19 % were child cases under 15 years, 7.44 % diagnosed with Grade 2 Disabilities and 43.3% were female cases, 2373 cases were under treatment and receiving MDT at the end of the fiscal year, marking a registered prevalence rate of 0.81 cases per 10,000 populations at the national level.
- There is a slight increase in prevalence rate of leprosy might be due to loosening of restrictions due to COVID 19 and continuation of field level activities such as active case detection, IEC/BCC campaigns etc.
- Madhesh province reported the highest PR of 1.43/10,000 population followed by Lumbini province (1.12). 16 districts have reported PR>1 per 10,000 population. 561 foreign cases from India were provided treatment in Nepal during FY 2078/79.
Disability inclusive health, rehabilitation, assistive technology and injury prevention
- EDCD/ LCDMS has aimed for a disability inclusive health system and population access to rehabilitation services and assistive technology. During FY 2078/79 (2021/22), we developed a Disability management and rehabilitation training
- package for primary health care providers and was piloted in Banke and Kaski. Post-COVID rehabilitation protocol, National standard on assistive technology and Operational guideline on priority assistive product list has been developed.
- Furthermore, the Systematic Assessment of Rehabilitation Situation (STARS) report was finalized and the Rapid Assistive
- Technology Assessment (rATA) was conducted in coordination with the National Health Research Center. Likewise, preliminary data was collected to evaluate the rehabilitation workforce using WHO standardized tools.
- Altogether 54,670 new cli- ents were reported in DHIS-2 have received rehabilitation service from 42 different hospitals and rehabilitation centers which shows an increment in data reporting compared to last fiscal year which was 29,814 clients.
- This is due to the fact that EDCD has initiated training to private rehabilitation service centers.
- Situation assessment and prioritization of strategic intersectoral actions in road safety and the National Policy Dialogue on road safety was organized highlighting the components of the safer system approach.
Zoonoses
- Nepal has a dual burden of disease and zoonotic diseases of epidemics; endemic and pandemic potentials are the major public health concerns. Globally more than 300 zoonotic diseases are identified among which about 60 have been identified in Nepal as emerging and re-emerging diseases.
- No people die of rabies or poisonous snake bites due to unavailability of anti-rabies vaccine (ARV) or anti-snake venom serum or timely health care services and to prevent, control and manage epidemic and outbreak of zoonosis is the goal of the zoonosis program.
- Around 75,000 cases in pets and more than human rabies cases occur each year with highest risk are in the terai.
- During FY 2078/79, a total of 85,483 dog and other animal bites cases have been reported throughout Nepal and a total of 9,346 snake-bites cases have been reported. Among cases 8,420 were non-poisonous and 926 were poisonous.
Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major public problem in Nepal.
- During this FY 2077/78, a total of 37,861 cases of TB were notified and registered at NTP.
- Among these, 98.5% (37,287) were incident TB cases (New and Relapse). Among all forms of TB cases 72.1 %were pulmonary TB, and out of them, 57.1% were pulmonary bacteriologically confirmed.
- Madhesh Province holds the highest proportion of TB cases (23.7%) followed by Bagmati province (23.3%). Kathmandu district alone holds around 42% (3,672 TB cases) of the TB cases notified from the Bagmati Province while its contribution is around 9.7% in the national total.
- In terms of eco-terrain distribution, Terai belt reported more than half of cases (22,904; 60.5%). Most cases were reported in the middle age group with the highest of 45.1% in 15 44 years of age.
- The childhood TB is around 8.7%. Out of total registered TB cases, there were 14,539 (38.4%) females and 23,322 (61.6%) males.
- The burden of TB can be measured in terms of incidence (defined as the number of new and relapse cases), prevalence and mortality. WHO estimates the current prevalence of all types of TB cases for Nepal at 117,000 (416/100,000) while the number of all forms of incidence cases (newly notified cases) is estimated at 69,000 (235/100,000).
- Case notification rate (CNR) of all forms of TB is 129/100,000 population whereas CNR for incident TB cases (new and relapse) is 72/100,000 population.
- Among drugs sensitive TB cases registered in FY 2077/78, 91.5% were treated successfully.
- There are estimated to be around 2,200 cases of DR-TB annually. However, 942 MDR TB cases are notified annually.
- In FY 2077/78, 659 RR/MDR-TB cases were registered for treatment. Among them, Lumbini Province is found to have higher burden followed by Madesh Province, Koshi Province, Bagmati Province, Sudurpaschim province, Gandaki Province, and Karnali Province respectively. Similarly, the burden of Pre-XDR and XDR TB patients was found more at Lumbini Province
- followed by Bagmati, Koshi, Madhesh, Sudurpaschim, Gandaki and Karnali provinces respectively.
- TB services were provided through 5,971 treatment centers. Regarding diagnostic services, there are 896 Microscopic
- centers and 93 GeneXpert centers throughout the country.
- DR-TB services were provided through 22 treatment centers and 81 Treatment Sub-centers.
- Though the DR-TB services are ambulatory, facility-based services were also provided through 2 TB treatment and referral management center 6 hostels and 1 DR home.
HIV/AIDS AND STI
- HIV/AIDS is a priority public health program of the Ministry of Health & Population (MoHP). Nepal remained as concentrated epidemic with prevalence rate 0.12% among adult population (15-49 years) and >5 % among key population i.e. MSM/ TG and PWID.
- The total estimated people living with HIV (PLHIV) is 30,300 in Nepal by 2021/22 (FY 2077/78), out of total estimated 4% are children (1,140) aged up to 14 years who are living with HIV in Nepal, while the adults aged 15 years and above account for 96%.
- Almost 65% of total estimated infections (19,460) among the population aged 15-49 years. By sex, males account for 55% of the total infections and the remaining infections are in females. Total 22,125 PLHIV are on ART treatment by the end of FY 2078/79.
Non-Communicable Diseases
- Non-communicable Diseases (NCDs) are emerging as the leading cause of deaths in Nepal due to changes in social determinants like unhealthy lifestyles, urbanization, demographic and economic transitions.
- The deaths due to NCDs (cardiovascular, diabetes, cancer and respiratory disease) have increased from 60% of all deaths in 2014 to 66% in 2018 (WHO Nepal Country Profile 2018).
- They are already killing more people than communicable diseases. Thus, Nepal has adapted and contextualized the PEN intervention for primary care in a low resource setting developed by WHO.
- The epidemic of non-communicable disease is recognized by UN and addressed in Sustainable Development Goal 3 i.e. “ensure healthy life and promote well-being for all at all ages” of this goal 3.4 targeted to “reduce by one third premature mortality from NCDs through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being”. PEN Implementation Plan (2016-2020) has been developed in line with the Multi-sectoral Action Plan for prevention and control of NCDs (2014-2020).
Mental Health
- Mental health and substance abuse are recognized as one of the health priorities and also addressed in Sustainable Development Goals (SDG). Within the health goal, two targets are directly related to mental health and substance abuse.
- Target 3.4 requests that countries: “By 2030, reduce by one third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being”. Target 3.5 requests that countries: “Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance abuse and harmful use of alcohol”. Nepal has a high burden of mental illness but there are limited interventions to address the epidemic of mental diseases.
Epidemiology and Outbreak Management
- Epidemiology and Outbreak Management involves working in the area of preparedness and response to outbreaks, epidemics and other health emergencies occurring in different parts of the country. It aligns with the organizational objective to reduce the burden of communicable diseases and unwanted health events through preparedness and responses during outbreak and epidemic situations by using the existing health care system and provides support to the Ministry of Health and Population (MoHP) for drafting national laws, policies, and strategies related to epidemiology and outbreak management. It provides subnational support for outbreak management and capacity building.
- Continuation of COVID-19 pandemic was seen in FY 2078/79. In the FY, a total of 318,724 PCR and 94,040 Antigen positive cases were registered.
- FY 2078/79 witnessed two cholera outbreaks, in Kapilvastu and Kathmandu Valley. A total of 1,914 Acute Diarrheal Disease (ADD) cases occurred in the outbreak in Kapilvastu district. Out of 21 stool samples tested for stool culture four stool samples tested positive for Vibrio Cholerae O1 Ogawa. Reactive Oral Cholera Vaccination (OCV) campaign was conduct- ed by Kapilvastu district in 10 municipalities.
- In Kathmandu valley, until Asar 32,2079, a total of 30 cases of cholera were reported of which 24, 4 and 2 cases were reported from Kathmandu, Lalitpur and Bhaktapur districts respectively.
Surveillance and Research
- Early Warning and Reporting System (EWARS) is a hospital-based sentinel surveillance system, established in 1997 – for early detection of six priority outbreak potential vector borne, water and food borne diseases/syndromes.
- Currently, 18 hospitals from all provinces and districts in the country have been selected as sentinel sites. Among 118, 13 sentinel
- sites reported consistently throughout the 52 epidemiological weeks in 2021 (FY 2077/78).
- Being the secretariat of National Drinking Water Quality Surveillance, EDCD conducts drinking water quality surveillance
- activities on a regular basis at national and sub-national level. In FY 2078/79 formation of provincial drinking water quality surveillance committee has been completed in the three provinces in this fiscal year and the rest four are planned in the next year.
- Monitoring of drinking water quality surveillance and water sample testing for microbiological parameters at sub-national and local level was performed with co-ordination through provincial health ministers/ directorates and associated offices.
- A single batch MTOT on water safety plan, drinking water quality surveillance and N-WASH (digita; tool for water supply and quality management) was conducted in this FY to strengthen and capacitate water quality surveillance at provincial and local level.
- In FY 2078/79, the call center received 132,687 calls, out of which 122,016 calls were answered and 17,939 times the Interactive Voice Response (IVR) were recorded.
- Alert and response System, pandemic response, general response and SMS service on epidemic and outbreak are the major scope of work of call center.
Health sector response to COVID-19 Pandemic
- The Government of Nepal intends to gradually immunize its citizens when vaccines become available, starting with the groups most at risk, in order to lower morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19.
- A total of 47,838,854 doses of COVID-19 vaccinations, including 6,873,016 additional doses, have been safely administered.
- There are now 108 RTPCR laboratories operating throughout all provinces (45.4% are private and 54.6% are public). Nepal recorded a total of 1,122,201 COVID-19 positive (including RT-PCR and Antigen test).
- The total case fatality rate is 1.2%, and the rate for people 60 and older is 6.3%. A total of 695,144 individuals have completed the QR certification.
Curative Services
- Minimum Service Standard (MSS) of health facilities is the service readiness tool designed to identify existing gaps towards the quality improvement of hospital services through self and joint assessment and developing an action plan scientifically.
- MSS has been implemented in 118 different levels of hospitals all over the country.
- There has been significant improvement in the service readiness status of the government hospitals since the implementation of MSS program and in the last two fiscal years the program has been expanded to health posts throughout the country.
Nursing and Social Security
Nursing Capacity Development
- The main responsibility of the nursing capacity development section is to facilitate in the process of development of plans, policies, strategies and programs for strengthening various specialties of nursing and midwives’ services.
- The major activities and achievements in FY 2078/079 were the school health and nursing program, development of five CPD modules and three clinical protocols, implementation of training on infection prevention and control based on a blended learning approach. In the FY 2078/079 community health nursing program was started in Bhaktapur and Bardibas Municipality.
- Similarly, in the FY 2078/079 onsite coaching and mentoring program was started.
Geriatric and Gender Based Violence Management
- The constitution of Nepal has ensured the right of the public to free basic health care service and emergency services.
- It has also ensured that the elderly people will be entitled to special protection from the nation and are entitled to the right to social security. So, to ensure the accessibility and utilization of health services by older people, the Ministry of Health and Population is extending the geriatric health care services to hospitals with more than 50 beds in this fiscal year.
- The geriatric services along with establishment of separate geriatric ward and outdoor services has been extended to 49 hospitals across the country in this fiscal year. Geriatric care center implementation guidelines and standards have been developed in which senior citizens with the many chronic health problems who need nursing care are the major service consumers.
- National policy dialogue program related to geriatric health was conducted. This section trained 80 Primary Health Care Professionals (Health assistants and staff nurses) related to Integrated care for elderly people and 14 medical officers for geriatric health care.
- Geriatric Review has been conducted among 24 geriatric service available hospitals.
- Gender-based Violence (GBV) is a grave human rights issue and public health concern which impacts the physical and mental health of the individual survivor and his/her children, and carries a social and economic cost to society.
- The Office of the Prime Minister and Council of Ministers developed a multi sectoral action plan to address the GBV issues in 2010 with celebration of international GBV years.
- In line with the action plan and to address needs of GBV survivors in an effective and efficient way MoHP established a hospital based One Stop Crisis Management Center(OCMC).
- In FY 2078/79, 88 OCMCs had been established in 77 districts. Orientation of the GBV program was conducted at three local levels. OCMC review was conducted in all provinces in FY 2078/79.
Deprived Citizen Treatment Support Program (Bipanna Nagarik Aushadhi Upchar Program)
- The Impoverished Citizens Service Scheme of Social Health Security Section provides the funding for impoverished Nepalese citizens to treat serious health conditions.
- Free treatment up to NPR 100,000 per patient via listed hospitals for severe diseases including cancer, heart disease, traumatic head injuries, traumatic spinal injuries, Alzheimer disease, Parkinson’s and sickle cell anemia diseases once in lifetime. Pre-transplant (HLA & cross match) test support up to NPR 50,000; renal transplantation costs up to NPR 400,000 per patient; medication costs up to NPR 100,000 for post-renal transplant cases; Free haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis services; and free medical treatment for acute kidney infections up to NPR 100,000.
- Till FY 2078/79 125,825 patients have received free treatment under impoverished citizens’ services scheme.
Female Community Health Volunteer (FCHV)
- The Government of Nepal initiated the Female Community Health Volunteer (FCHV) Program in 2045/46 (1988/1989) in 27 districts and expanded it to all 77 districts thereafter. 51,423 FCHVs recruited a total of 49,605 (as reported in HMIS) FCHVs are actively working in Nepal. In the fiscal year 2077/078 biannual FCHV review meeting was held at local and FCHV day was celebrated.
- The major role of FCHVs is to advocate healthy behavior among mothers and community people to promote safe motherhood, child health, for family planning and other community-based health issues and service delivery.
- FCHVs distribute condoms and pills, ORS packets and vitamin A capsules, treat pneumonia cases (only in the selected remote area where referral is not possible), refer serious cases to health facilities and motivate and educate local people on healthy behavior related activities. They also distribute iron tablets to pregnant women.
Reimbursement program for free treatment of Janayudhha, Jana-andolan ghaite, Madhesh terai ghaite, Bhukampa pidit.
- The program provides reimbursement to the government and community hospitals that claim an amount equal to the free services they have provided to the casualties of various peoples movement and earthquake affected peoples based recommendation by the government authorities stating their casualty status.
- In FY 2078/79 a total of 2,500,000 rupees budget was allocated for the program and reimbursement were given to three hospitals that claimed the amount.
Reimbursement to the hospitals for free treatment of Acid Attack Victims
- The program provides reimbursement to the four dedicated hospitals that provide free treatment to the acid attack victims. The program covers ambulance expenses, food expenses of the victim and care-taker, in-patient charges, medical and procedure expenses as well as long term medications that must be used by the patients. In FY 2078/79 total budget of 700,000 was provided to the hospitals for treatment of three victims.
Trainings conducted regarding hemodialysis
- In FY 2078/79 two categories of training were conducted under hemodialysis specialty. Hemodialysis training for nurses was conducted in two batches with 20 participants in each batch yielding 40 hemodialysis specialist nurses.
- Same-way users training for hemodialysis equipment maintenance was conducted in one batch with 10 participants.
Inpatients/OPD services
- For the fiscal year, 2078/79 inpatient and outpatient services were provided by all types and levels of hospitals. A total of 1,548,336 patients were admitted to the hospitals. The highest admissions were due to pregnancy, childbirth and
- puerperium which accounted for more than 20% of discharged cases. The inpatient hospital death rate was 1.08%. In
- addition, the number of emergency visits was also increasing as 2,938,849 patients received emergency care. Outpatient morbidity has been reported in 19 different sections that cover 232 diseases including communicable diseases,
- non-communicable diseases, injuries, organ-specific diseases, and mental health problems. Although the majority of tertiary hospitals and private hospitals had not reported outpatient morbidity throughout the year, the maximum OPD cases were related to headaches followed by upper respiratory tract infection (URTI).
Human Organ Transplant Services
- Shahid Dharma Bhakta National Transplant Center (SDBNTC) was established in 2012 by the Ministry of Health and Population to strengthen and expand organ transplantation services in the country. This center started its services merely with the OPD services, but within a few years of its establishment it has extended its services beyond organ transplantation.
- The number of patients in all these aspects has increased remarkably in FY 2078/79. There were 47,047 patients served in the outpatient department, while the number of admission and discharge were almost similar with 2,106 and 2,099 respectively.
- There were 972 minor surgeries and 827 major surgeries in FY 2078/79. The number of kidney transplantations escalated from 49 to 160 in FY 2078/79. The number of sessions of paid dialysis decreased from 2,940 in FY 7078/79 to 2,526 in fiscal year 2077/78.
- There has been a slight increase in free dialysis sessions in FY 2078/79. The number of lab tests done in FY 2078/79 was 160,537.
Pashupati Homoeopathic services
- Pashupati Homoeopathic Hospital is the only hospital providing homeopathic services to the people of Nepal in the public sector. The homeopathic system is economical, easy and has no adverse effects. The hospital provides OPD service only.
- The number of patients receiving homoepptathic services is increasing. Many referred cases are also treated here like allergic rhinitis, urticaria, laryngeal papilloma, PCOD and other skin diseases. People of Kathmandu valley and nearby districts can take free and convenient service at the hospital.
- However, People far from Kathmandu valley are not able to take benefits provided by this hospital. It is essential to provide service in all seven provinces of Nepal with utmost priority.
National Health Training
- The training network includes seven provincial health training centers and 60 clinical training sites.
- It is also responsible for accrediting clinical training sites and Clinical and public health related training courses to maintain the standard of the health training so as to strengthen the capacity of health service providers across the country.
Vector Borne Disease Research & Training
- In the FY 2078/79 Vector Borne Diseases Trainings (VBDs) for VBDs focal persons/health workers, malaria microscopic basic and refresher trainings for lab technicians and lab assistants were conducted to enhance their level of knowledge and skills related with prevalent vector borne diseases. Studies conducted during this fiscal year include monitoring of insecticide resistance in malaria vectors and transmission assessment survey of Lymphatic Filariasis.
- During the FY 2078/79 VBDRTC conducted Re Pre TAS in Morang, Kailali, Banke, Kapilvastu and Dang districts, TAS-I in Bardiya and Dhankuta districts, and TAS-II in Darchula, Baitadi, Bajhang, Doti, Dadeldhura, Achham, Bajura, Dailekh, Surkhet, Jajarkot, Sunsari, Terhathum, Bhojpur and Udayapur districts.
Health, Education, Information and Communication
- NHEICC has been taking a leading role in the SAFER initiative.
- In the fiscal year 2078/79 major programme conducted by NHEICC was Tobacco control programme under which advocacy for Tobacco control and regulation with local leaders, journalist interaction and health tax fund programme activities were conducted. NHEICC launched the SAFER initiative for alcohol control and intensive RCCE activities were conducted.
- It conducted national level campaigns like mask campaign, mental health wellbeing campaign, and COVID-19 vaccination campaign.
- Likewise, advocacy and awareness programmes of health promotion for Samriddha Nepal, FP, RH morbidity, Safe motherhood and newborn care, nutrition child health, immunization, communicable disease, eye health, oral health, environmental health, RTI, mental health andNCDs through mass media and community engagement was carried out.
- Similarly, NHEICC used a digital platform to disseminate health related messages and information.
Health Laboratory Services
- In FY 2078/79, major public health related activities carried out through NPHL were laboratory-based surveillance of Japanese encephalitis, measles/rubella, polio, antimicrobial resistance (AMR) of selected bacteria, influenza etc.
- Apart from public health related activities, it has provided results of thousands of routine and specialized tests from various
- departments. NPHL is highly dedicated to quality service. For this it has implemented a two-way LIS system integrating collection, testing machine and reporting, which has dramatically minimized the human errors and effectiveness can be Felt in reports provided by NPHL.
- National External Quality Assessment Scheme (NEQAS), one of the oldest programs related to quality service, has been running through NPHL since 1987.
- In this program, NPHL prepares various proficiency test panels and dispatches to participating laboratories throughout the country and analyzes their quality based on the received results from them.
- Currently more than 600 labs have enrolled in this program. Among them around 400 are private labs and the remaining are government labs. On the other hand, to monitor the service quality of its own, NPHL has participated in various
- international External Quality Assessment Scheme (IEQAS) run by renowned institution of the glove like: CMC Vellore,
- Birmingham IEQAS, Mahidol university hospital, Sriraaj hospital etc. The blood bank bureau of NPHL supports and regulates the blood banks throughout the country as well as organizes various workshops on planning and managing blood
- transfusion service. It also supports blood banks for their capacity building.
- In order to provide super specialized service, a flow cytometry lab has been established in NPHL. It provides the diagnosis of various cancers with its modern equipment and cutting-edge technologies.
- HLA typing lab is also in full operation which has helped many patients by providing diagnostic requirements for organ transplant at a very reasonable price.
- Similarly, an immunohistochemistry lab has been installed and is about to provide service soon. Triple marker and quadruple marker tests are also performed on a regular basis which has helped for screening of genetic abnormalities in fetuses.
Health Service Management:
- Procuring, and distributing health commodities for the health facilities and the monitoring and evaluation of health programs. The division is also responsible for monitoring the quality of air, environmental health, health care waste management, water and sanitation.
Logistics Management
- The major activities conducted by the IHIMS section in FY 2078/79 are approval of IHIMS’s Roadmap (2022-2030), comprehensive revision of HMIS tools (73 tools), orientation on the revised HMIS tools (M-ToT:89 participants, D-ToT: 168, local level Training: 1,522), DHIS2 dashboard program expanded to 33 LLGs, implementation and training on ICD 11, estimation of target population up to ward level, assessment of routine data quality (RDQA) in five districts (Morang, Dhanusha, Dhading, Tanahu, Pyuthan), preparation and publication of DoHS annual report, initiation of national data warehouse, initiation of DHIS 2 Upgrade from version 2.30 to 2.38, Health Infrastructure Information System (HIIS) integration process. Online self-reporting has been increased from 2,517 to 3,779 from previous FY 2077/78 to this FY 2078/79.
- The major activities conducted for the FY 2078/79 were the revision of the LMIS form and Basic Logistics Training Manual, data quality assessment, review and optimization of information flow for the LMIS report, conduction of eLMIS training, implementation/ expansion of eLMIS sites, support through help desk, development and implementation of standard operating procedures (SOPs) for the functionality of the eLMIS along with eLMIS monitoring and data utility for decision making.
Personnel Administration
- The Personnel Administration Section (PAS) is responsible for routine and program administrative function. Its major functions include upgrading health institutions (O&M), the transfer of health workers, level upgrading of health workers up to 7th level, capacity building as well as internal management of human resources of personnel.
Financial Management
- The preparation of annual budgets, the timely disbursement of funds, accounting, reporting, and auditing are the main.
- Out of the total National Budget of Rs. 1,647,576,700,000.00 a sum of Rs. 90,754,500,000 (5.50%) was allocated for the health sector during the fiscal year 2078/79. Of the total health sector budget, Rs. 43,276,927,000.00 (47.68%) was allocated for the execution of programs under the Department of Health Services with COVID-19 control and management.
Medico-legal Services
- it is high time for the Nepal Government to facilitate the environment to utilize those experts in the medico-legal field for providing their specialist service to Nepali people.
- During the last FY, a number of activities related to medico-legal services were conducted by DoHS and the Ministry of Social Development (Karnali Province).
- Around 200 doctors working at the periphery were benefited by these orientation and skill enhancing training.
Monitoring and Evaluation
- The Nepal Health Sector Strategy (NHSS) 2015-2022 focuses on better access to and use of information with ICT. It also emphasizes improved and interoperable routine information systems and prioritizes surveys and research for informed decision-making and better policy and planning processes. The strategy promotes upgraded and integrated health sector reviews at various levels that feed into the planning and budgeting process.
Health Councils
- The six professional health councils (Nepal Medical Council, Nepal Nursing Council, NepalAyurvedic Medical Council, Nepal Health Professional Council, Nepal Pharmacy Council and Nepal Health Research Council) accredited more effectively the health services, training, research and regulated care providers managed in a scientific manner.
Health Insurance
- Health Insurance is a social health security program from the Government of Nepal which aims at enabling its citizens with the access of quality health care services without placing a financial burden on them. In the beginning of FY 2072/73, it was run under the Social Health Development Committee, however since FY 2074/75, it has been running under the Health Insurance Board (HIB) guided by Health Insurance Act and Regulation. The Health Insurance program.
- in FY 2073/74. At the end of FY 2076/77, the program was implemented in 58 districts of the country. Till the end of
- FY 2078/79, the program was implemented in all 77 districts and 746 Local levels of the country.
- The total cumulative numbers of enrolled people are 6,045,192 and total renewed insures are 3,451,951 at the end of FY 2078/79. During this
- FY, the total population coverage of the health insurance program is 22.52%. Among the total insured, about 4,248,606
- people were active in the health insurance program in FY 2078/79. The leading top five districts based on the number of new enrollments are Jhapa, Sunsari, Morang, Chitwan and Kailali.
Development Partners Support in Health Programs
- The outcomes discussed in the previous chapters are the results of combined efforts of the Ministry of Health and Population (MoHP), various development partners (multilateral, bilateral) and other supporting organizations including international organizations and national NGOs and private sectors. The Department of Health Services acknowledges its partnership with these organizations and their large contributions to Nepal’s health sector. This chapter lists the focus of these organizations’ various programs. Partners have also provided technical assistance in their areas of expertise.
- In the current sector programme, the World Bank has allocated all its commitment through a Program-for-Results, a tool which disburses funds against a verifiable set of results, called Disbursement Linked Results (DLRs). UKAid and GAVI are also disbursing part of their commitments against some DLRs identified and agreed with the MoHP. In addition, in the Fiscal Year 2021/2022, Development Partners continued to provide additional funding, in-kind and technical support to the MoHP for the preparedness and response to COVID-19 pandemic.

Related documents
- Nepal Health Sector Strategic Plan 2023-2030
- Annual Report of the Department of Health Services (DoHS) 2077/78
- Glimpse of Annual Report Department of Health Services 2073/74 (2016/17)
- Annual report of the Department of Health Services (DoHS) 2073/74 (2016/2017)
- Annual Report Department of Health Services 2072/73 (2015/2016)
- Annual Report of the Department of Health Services (DoHS) – 2071/72 (2014/2015)
- Annual Report of DOHS 2070/71 (2013/2014)
- Annual Report of DoHS 2069/2070 (2012-2013)
- National Annual Review, MoHP – 2017/18 (Presentation Slides)
- Health Sector Progress Report 2018, Ministry of Health & Population
- Glimpse of Annual Report Department of Health Services 2073/74 (2016/17)
- Key Findings (Nepali & English) – The 2016 Nepal Demographic and Health Survey (2016 NDHS)
- Nepal Health Sector Strategy(NHSS) Implementation Plan 2016-21


