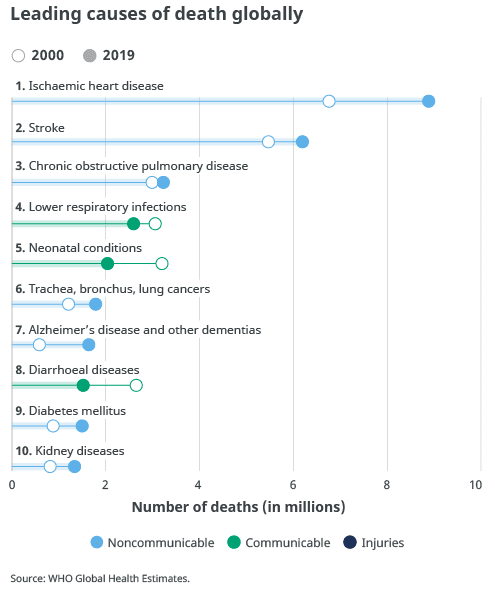
Noncommunicable diseases now make up 7 of the world’s top 10 causes of death, according to WHO’s 2019 Global Health Estimates, published today. This is an increase from 4 of the 10 leading causes in 2000. The new data cover the period from 2000 to 2019 inclusive.
In 2019, the top 10 causes of death accounted for 55% of the 55.4 million deaths worldwide.
The top global causes of death, in order of total number of lives lost, are associated with three broad topics: cardiovascular (ischaemic heart disease, stroke), respiratory (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lower respiratory infections) and neonatal conditions – which include birth asphyxia and birth trauma, neonatal sepsis and infections, and preterm birth complications.
Causes of death can be grouped into three categories: communicable (infectious and parasitic diseases and maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions), noncommunicable (chronic) and injuries.
Leading Causes of death globally
- Ischaemic heart diseases
- Stroke
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases
- Lower Respiratory Infections
- Neonatal conditions
- Trachea, bronchus, lung cancers
- Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias
- Diarrhoeal diseases
- Diabetes mellitus
- Kidney diseases
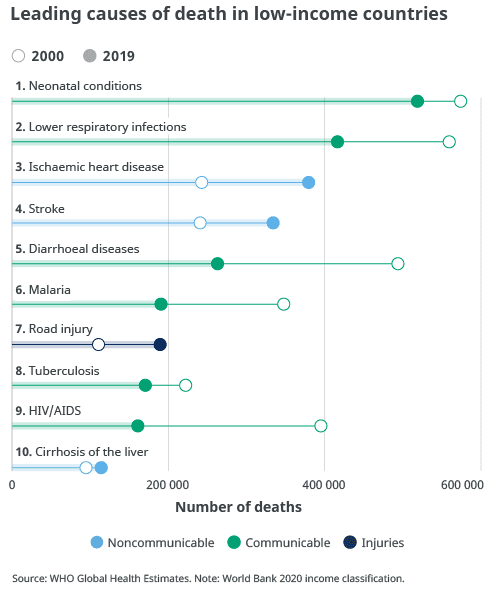
Global decline in deaths from communicable diseases, but still a major challenge in low- and middle-income countries
In 2019, pneumonia and other lower respiratory infections were the deadliest group of communicable diseases and together ranked as the fourth leading cause of death. However, compared to 2000, lower respiratory infections were claiming fewer lives than in the past, with the global number of deaths decreasing by nearly half a million.
Leading causes of death in low-income countries
- Neonatal conditions
- Lower respiratory infections
- Stroke
- Diarrhoeal diseases
- Malaria
- Road injury
- Tuberculosis
- HIV/AIDS
- Cirrhosis of the Liver
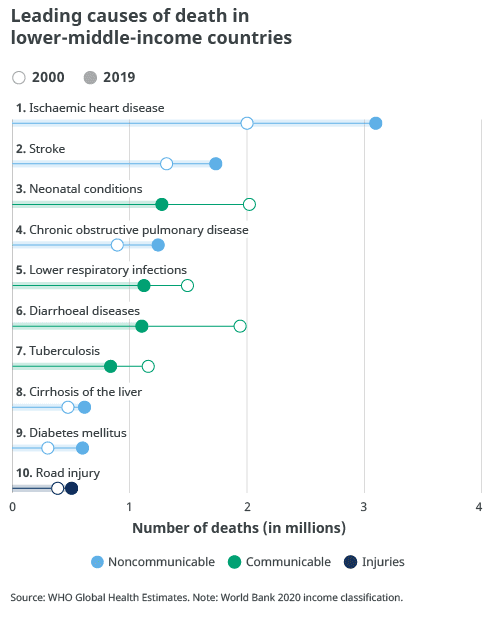
Leading causes of death in lower-middle-income countries
- Ischaemic heart diseases
- Neonatal conditions
- COPD
- Lower respiratory infections
- Diarrhoeal diseases
- Tuberculosis
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Diabetes mellitus
- Road injury
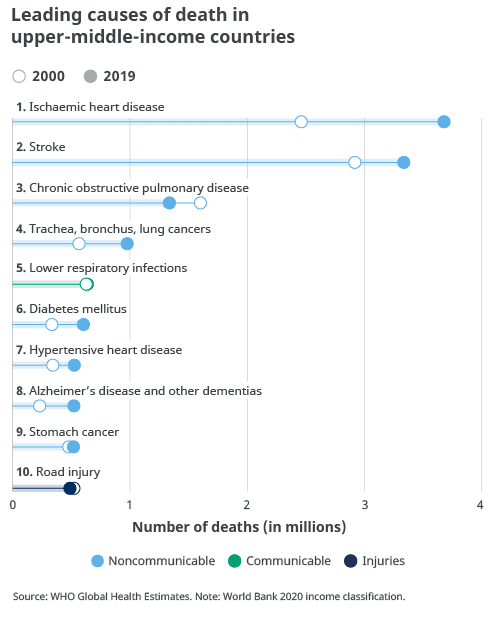
Leading causes of death in upper-middle-income countries
- Ischemic heart diseases
- Stroke
- COPD
- Trachea, bronchus, lung cancers
- Lower respiratory infections
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertensive heart disease
- Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias
- Stomach cancer
- Road injury
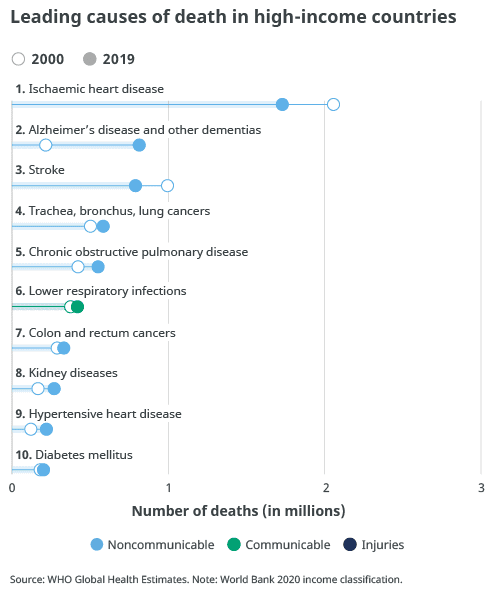
Leading causes of death in high-income countries
- Ischaemic heart disease
- Alzheimer’s diseases and other dementias
- Trachea, bronchus, lung cancers
- COPD
- Lower respiratory infections
- Colon and rectum cancers
- Kidney diseases
- Hypertensive heart disease
- Diabetes Mellitus
OFFICIAL LINK: WHO
Do you have a website? Looking for the best hosting provider? Here’s a discount code.
Latest Public Health Jobs
Latest Posts
- Multisectoral Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of NCDs, 2026-2030 (Draft)
- National Standard Operating Procedure for Early Warning, Alert and Response System (EWARS), 2025
- Priority Infectious Diseases for Community-Based Surveillance in Nepal
- Community Based Disease Surveillance Guideline, 2082
- Political declaration of the fourth high-level meeting of the General Assembly on the prevention and control of NCDs and the promotion of mental health and well-being
Thanks for visiting us.
Disclaimer: The resources, documents, guidelines, and information on this blog have been collected from various sources and are intended for informational purposes only. Information published on or through this website and affiliated social media channels does not represent the intention, plan, or strategies of an organization that the initiator is associated with in a professional or personal capacity, unless explicitly indicated.
If you have any complaints, information, or suggestions about the content published on Public Health Update, please feel free to contact us at blog.publichealthupdate@gmail.com.
#StayUpdated


