The Nepal health professional council (NHPC) has published a Syllabus for Licensing Examination of Master of Public Health (MPH) 2021.
Subjects/areas/domains
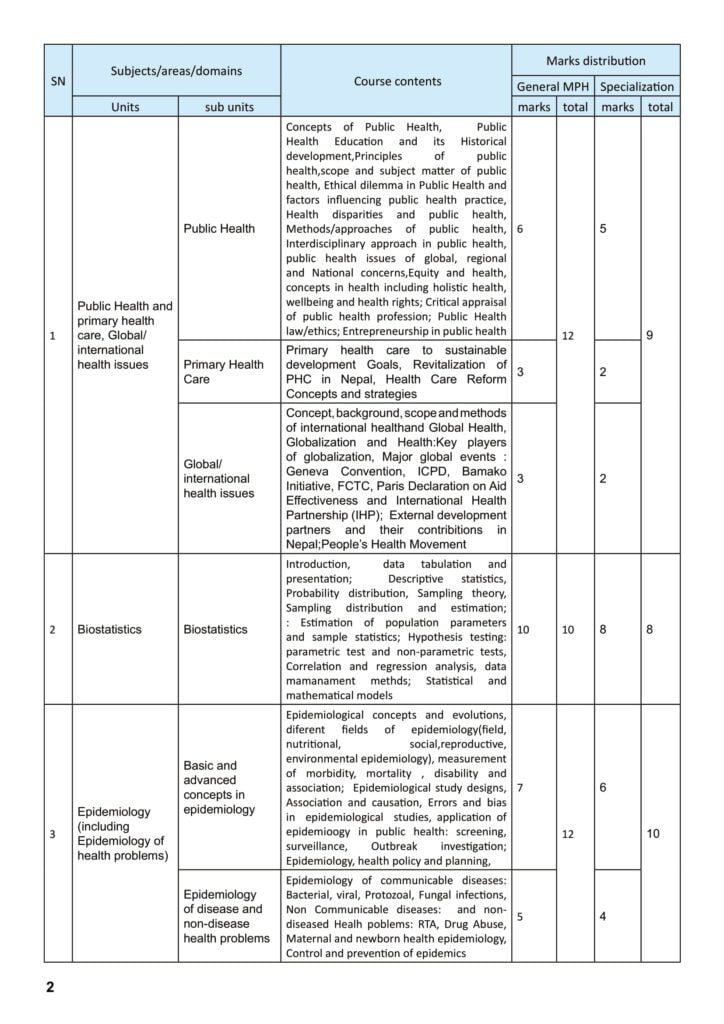
A. Public Health and primary health care, Global/ international health issues
1. Public Health: Concepts of Public Health, Public Health Education and its Historical development,Principles of public health,scope and subject matter of public health, Ethical dilemma in Public Health and factors influencing public health practice, Health disparities and public health, Methods/approaches of public health, Interdisciplinary approach in public health, public health issues of global, regional and National concerns,Equity and health, concepts in health including holistic health, wellbeing and health rights; Critical appraisal of public health profession; Public Health law/ethics; Entrepreneurship in public health.
2. Primary Health Care: Primary health care to sustainable development Goals, Revitalization of PHC in Nepal, Health Care Reform Concepts and strategies.
3. Global/ international health issues: Concept, background, scope and methods of international health and Global Health, Globalization and Health:Key players of globalization, Major global events : Geneva Convention, ICPD, Bamako Initiative, FCTC, Paris Declaration on Aid Effectiveness and International Health Partnership (IHP); External development partners and their contributions in Nepal;People’s Health Movement.
B.Biostatistics
1. Biostatistics: Introduction, data tabulation and presentation; Descriptive statistics, Probability distribution, Sampling theory, Sampling distribution and estimation; : Estimation of population parameters and sample statistics; Hypothesis testing: parametric test and non-parametric tests, Correlation and regression analysis, data management methods; Statistical and mathematical models.
C. Epidemiology (including Epidemiology of health problems)
1. Basic and advanced concepts in epidemiology: Epidemiological concepts and evolutions,
different fields of epidemiology(field, nutritional, social,reproductive, environmental epidemiology), measurement of morbidity, mortality , disability and association; Epidemiological study designs, Association and causation, Errors and bias in epidemiological studies, application of epidemiology in public health: screening, surveillance, Outbreak investigation; Epidemiology, health policy and planning.
2. Epidemiology of disease and non-disease health problems
Epidemiology of communicable diseases: Bacterial, viral, Protozoal, Fungal infections, Non Communicable diseases: and non diseased Health problems: RTA, Drug Abuse, Maternal and newborn health epidemiology, Control and prevention of epidemics.
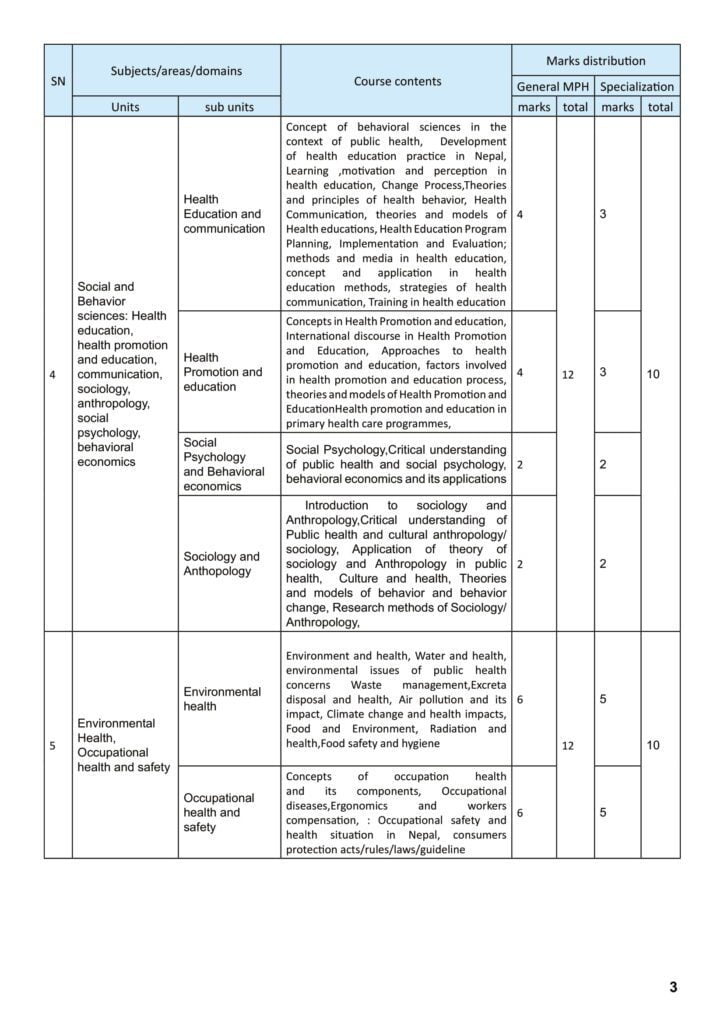
D. Social and Behavioral sciences: Health education, health promotion and education, communication, sociology, anthropology, social psychology, behavioral economics
- Health Education and communication: Concept of behavioral sciences in the context of public health, Development of health education practice in Nepal, Learning ,motivation and perception in health education, Change Process,Theories and principles of health behavior, Health Communication, theories and models of Health educations, Health Education Program Planning, Implementation and Evaluation; methods and media in health education, concept and application in health
education methods, strategies of health communication, Training in health education. - Health Promotion and education: Concepts in Health Promotion and education, International discourse in Health Promotion and Education, Approaches to health promotion and education, factors involved in health promotion and education process, theories and models of Health Promotion and Education Health promotion and education in primary health care programmes.
- Social Psychology and Behavioral economics: Social Psychology,Critical understanding of public health and social psychology, behavioral economics and its applications.
- Sociology and Anthropology: Introduction to sociology and Anthropology,Critical understanding of Public health and cultural anthropology/ sociology, Application of theory of sociology and Anthropology in public health, Culture and health, Theories and models of behavior and behavior change, Research methods of Sociology/ Anthropology.
E. Environmental Health, Occupational health and safety
- Environmental health: Environment and health, Water and health, environmental issues of public health concerns Waste management,Excreta disposal and health, Air pollution and its impact, Climate change and health impacts, Food and Environment, Radiation and health,Food safety and hygiene.
- Occupational health and safety: Concepts of occupation health and its components, Occupational diseases,Ergonomics and workers compensation, : Occupational safety and health situation in Nepal, consumers protection acts/rules/laws/guideline.
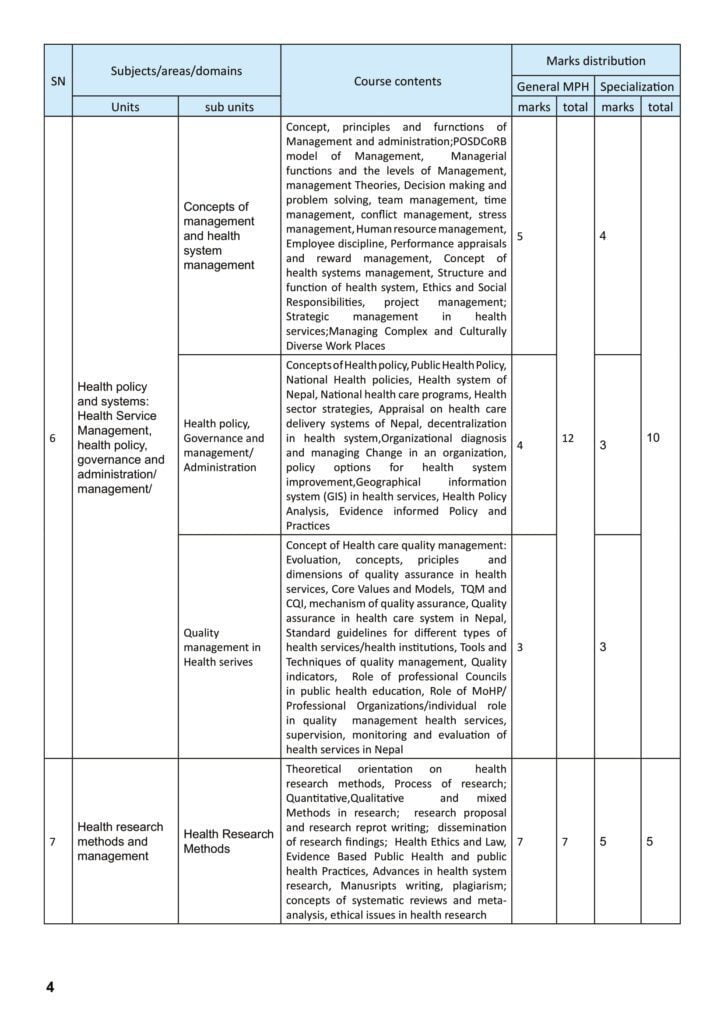
F. Health policy and systems: Health Service Management, Health policy, governance and administration/ management
1. Concepts of management and health system management: Concept, principles and functions of Management and administration;POSDCoRB model of Management, Managerial functions and the levels of Management, management Theories, Decision making and problem solving, team management, time management, conflict management, stress management, Human resource management, Employee discipline, Performance appraisals and reward management, Concept of health systems management, Structure and function of health system, Ethics and Social Responsibilities, project management; Strategic management in health services; Managing Complex and Culturally Diverse Workplaces.
2. Health policy, Governance and management/ Administration: Concepts of Health policy, Public Health Policy, National Health policies, Health system of Nepal, National health care programs, Health sector strategies, Appraisal on health care delivery systems of Nepal, decentralization in health system,Organizational diagnosis and managing Change in an organization, policy options for health system improvement,Geographical information system (GIS) in health services, Health Policy Analysis, Evidence informed Policy and Practices.
3. Quality management in Health services: Concept of Healthcare quality management: Evolution, concepts, principles and dimensions of quality assurance in health services, Core Values and Models, TQM and CQI, mechanism of quality assurance, Quality assurance in health care system in Nepal, Standard guidelines for different types of health services/health institutions, Tools and Techniques of quality management, Quality indicators, Role of professional Councils in public health education, Role of MoHP/ Professional Organizations/individual role in quality management health services, supervision, monitoring and evaluation of health services in Nepal.
G. Health research methods and management
1. Health Research Methods: Theoretical orientation on health research methods, Process of research; Quantitative,Qualitative and mixed Methods in research; research proposal and research report writing; dissemination of research findings; Health Ethics and Law, Evidence Based Public Health and public health Practices, Advances in health system research, Manuscripts writing, plagiarism; concepts of systematic reviews and meta analysis, ethical issues in health research.
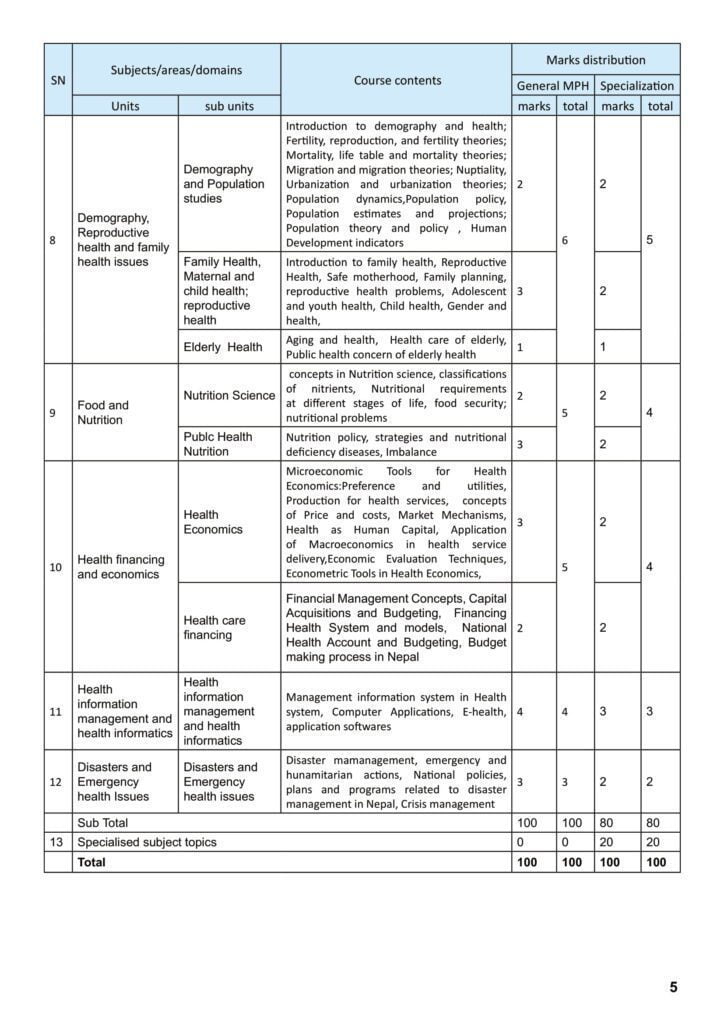
H. Demography, Reproductive health and family health issues
1. Demography and Population studies: Introduction to demography and health; Fertility, reproduction, and fertility theories; Mortality, life table and mortality theories; Migration and migration theories; Nuptiality, Urbanization and urbanization theories; Population dynamics,Population policy, Population estimates and projections; Population theory and policy , Human Development indicators.
2. Family Health, Maternal and child health; reproductive health: Introduction to family health, Reproductive Health, Safe motherhood, Family planning, reproductive health problems, Adolescent and youth health, Child health, Gender and health,
3. Elderly Health: Aging and health, Health care of elderly, Public health concern of elderly health.
I. Food and Nutrition
1. Nutrition Science concepts in Nutrition science, classifications of nutrients, Nutritional requirements at different stages of life, food security; nutritional problems
2. Public Health Nutrition: Nutrition policy, strategies and nutritional deficiency diseases, Imbalance.
J. Health financing and economics
- Health Economics: Microeconomic Tools for Health Economics:Preference and utilities, Production for health services, concepts of Price and costs, Market Mechanisms, Health as Human Capital, Application of Macroeconomics in health service delivery,Economic Evaluation Techniques, Econometric Tools in Health Economics, Health care
financing - Financial Management: Concepts, Capital Acquisitions and Budgeting, Financing Health System and models, National Health Account and Budgeting, Budget making process in Nepal.
K. Health information management and health informatics
1. Health information management and health informatics: Management information system in Health system, Computer Applications, E-health, application softwares
L. Disasters and Emergency health Issues
1. Disasters and Emergency health issues: Disaster management, emergency and humanitarian actions, National policies, plans and programs related to disaster management in Nepal, Crisis management.
Do you have a website? Looking for the best hosting provider? Here’s a discount code.
Latest Public Health Jobs
Latest Posts
- National workforce capacity for essential public health functions: Operational handbook for country-led contextualization and implementation
- World Conference on Lung Health Travel Grants 2025
- GIS Training Manual for Health Statistics
- WHO launches bold push to raise health taxes and save millions of lives
- National Oral Health Strategy 2081-2087
Thanks for visiting us.
Disclaimer: The resources, documents, guidelines, and information on this blog have been collected from various sources and are intended for informational purposes only. Information published on or through this website and affiliated social media channels does not represent the intention, plan, or strategies of an organization that the initiator is associated with in a professional or personal capacity, unless explicitly indicated.
If you have any complaints, information, or suggestions about the content published on Public Health Update, please feel free to contact us at blog.publichealthupdate@gmail.com.
#StayUpdated


