The World Obesity Federation has published the 2021 Atlas on COVID-19 and Obesity which shows increased bodyweight is the second greatest predictor of hospitalisation and a high risk of death for people suffering from COVID-19. Only old age rates as a higher risk factor.
WORLD OBESITY DAY: WE NEED TO ACT TOGETHER, NOW!
World obesity day 2020: ‘Every Body Needs Everybody.’
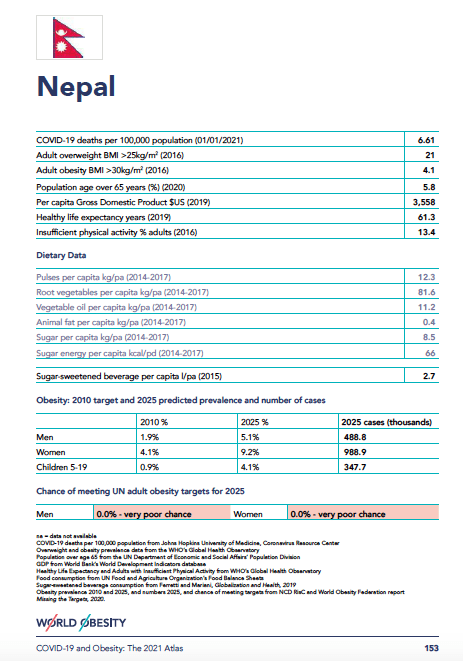
Country fact sheet: Nepal
World Obesity Federation’s ROOTS: A Call for Action
Building stronger economies by investing in health
The COVID-19 pandemic has shown that a societal, worldwide response to a disease is possible.
COVID-19 has also exposed the imperative to address other global health challenges such as obesity. Evolving evidence on the close association between COVID-19 and underlying obesity provides a new urgency – and inspiration- for political and collective action.
Obesity is a disease that does not receive prioritisation commensurate with its prevalence and impact, which is rising fastest in emerging economies. It is a gateway to many other noncommunicable diseases and mental-health illness and is now a major factor in COVID-19 complications and mortality. There is a window of opportunity to advocate for, fund and implement these actions in all countries to ensure better, more resilient and sustainable health for all, now and in our postCOVID-19 future.
This Declaration is inspired by calls from the World Health Organization, the United Nations and the OECD to ‘build back better’ from COVID-19, to improve the health of people and the planet. It reflects a consensus reached at the 2020 Global Obesity Forum.
A ROOTS approach
On World Obesity Day 2020, the global obesity community came together to acknowledge the complexity of obesity and to develop the ROOTS framework, which sets out an integrated, equitable, comprehensive and person-centred approach to addressing obesity. Building on the ROOTS framework, this Declaration sets out recommendations for immediate action across the obesity spectrum from prevention to treatment, within the context of COVID-19:
R- Recognise that obesity is a disease in its own right as well as a risk factor for other conditions, including significantly worsening the outcomes of COVID-19 infection. We call for:
– people living with obesity to be included among the groups prioritised for testing and vaccination;
– spaces in which people living with obesity receive COVID-19 care to be appropriately equipped, with trained health workers free from weight bias, who have knowledge on the complexity of obesity and obesity care needs;
– the recognition that, in many contexts, COVID-19 and obesity are linked through inequity/health disparities, and strategies to address both diseases should adopt a social determinants of health approach.
O- Obesity monitoring and surveillance must be enhanced to strengthen effective strategies for preventing and treating obesity. We call for:
– population-wide monitoring to assess how COVID-19 has affected the risk factors for and prevalence of obesity;
– monitoring of availability and accessibility to nutritionally adequate food supplies, especially among populations vulnerable to COVID-19 including those with obesity;
– monitoring the impact of policies and restrictions to limit the spread of COVID-19 for their impact on people with obesity;
– monitoring of compliance with the international code and resolutions on marketing of breastmilk substitutes, as there is evidence of violations occurring.
O- Obesity prevention strategies must be developed, tested and implemented across the life course, from
pre-conception, through childhood, and into older age. We call for:
– primary and secondary obesity prevention efforts to be continued and enhanced for all without discrimination, as a critical means to increase population resilience to pandemics;
– co-creation and implementation of policies to reduce childhood obesity, working with young people and acknowledging that, for many children, COVID-19 control measures have increased risk;
– equity-based obesity prevention strategies focusing on populations most affected by the syndemic interactions between COVID-19, poverty and race.
T- Treatment of obesity – including behavioural, pharmacological, digital, nutritional, physicalactivity based and surgical interventions – should be accessible to all people with obesity. We call for:
– routine obesity treatment and management services not to be restricted during COVID-19, but instead invested in and prioritised to enhance equitable access;
– development of novel treatment strategies (for example, tele-medicine) to include solutions co-created with the participation of people living with obesity, including those with ‘long’ COVID.
S- Systems-based approaches should be applied to the treatment and prevention of obesity. In the recovery from COVID-19 we call for action across the following systems:
– Health: Cost-effective community-based prevention, including monitoring and screening should be integrated with clinical pathways for secondary prevention, obesity management and treatment.
– Food: National and local government-led action and incentives to pivot food systems towards sustainable growth models, focusing on ‘triple win’ policy solutions to address the Global Syndemic of over- and undernutrition and climate change.
– Transport: Investment in active transport systems to promote physical and mental health, while reducing COVID-19 transmission risk and mitigating climate change.
– Water and sanitation: Universal access to clean water, especially in countries where sugarsweetened beverages may be more widely available than safe drinking water.
– Education: Provision of nutritious school meals, particularly for socioeconomically disadvantaged children, and the replacement of such meals when schools are closed; increased physical education.
-Economic: Novel investment from global health donors and multilateral institutions to address the rising cost of obesity in lower income countries.
Recommended reading
- World Obesity Day: We need to act together, now!
- Portugal brings down obesity by taxing sugary drinks
- World Obesity Day: The Roots of Obesity Run Deep
- Obesity-Related Diseases Among Top Three Killers in Most Countries, World Bank Says
- 6 keys to ending childhood obesity
- #WorldObesityDay 2017 is focusing on tackling the causes of #obesity to avoid #NCDs
- Kidney Disease & Obesity – Healthy Lifestyle for Healthy Kidneys! #worldkidneyday #move4kidneys!
- 6 Recommendations of ECHO to reversing the rising trend of childhood obesity and overweight
- World Health Statistics 2020: Monitoring health for the SDGs



Comments are closed.